
However, FTP clients shouldn’t rely on the default values, as this is unsecure. If the client fails to issue a PASV command, the Data Connection defaults to port 20. In the Passive Mode, the client issues a PASV command to indicate that it will wait “passively” for the server to supply an IP and port number, after which the client will create a Data Connection to the server. In passive mode FTP, the client initiates both connections to the server, solving the problem of firewalls filtering the incoming data port connection to the client from the server. Once the FTP client receives a port, it starts the second connection and sends data. Here, the client connects and sends the PASV command, which functions as a request for a port number to connect to. Passive FTP: This is also referred to as passive mode or PASV and it was developed to resolve the issue of servers initiating the connection to the client. In an Active Mode FTP, the client issues a PORT command to the server signaling that it will “actively” provide an IP and port number to open the Data Connection back to the client. In an active mode connection, when the client makes the initial connection and sends PORT, the server will then connect back to the client’s specified data port from its local data port, which is port 20. That is, when a client and server intend to transfer data, they usually start a control connection first in order to negotiate the details of the Data Connection prior to opening it and transferring data. In this mode, the FTP client connects from a random port (n-1023) to the FTP server’s command port (21). You may also want to see this guide: Warning: FTP over TLS is not enabled, users cannot securely log in: You appear to be behind a NAT Router, please configure the passive mode settings and forward a range of ports in your router.Īctive FTP: This was originally the only method of FTP and is therefore often the default mode for FTP.
Filezilla login how to#
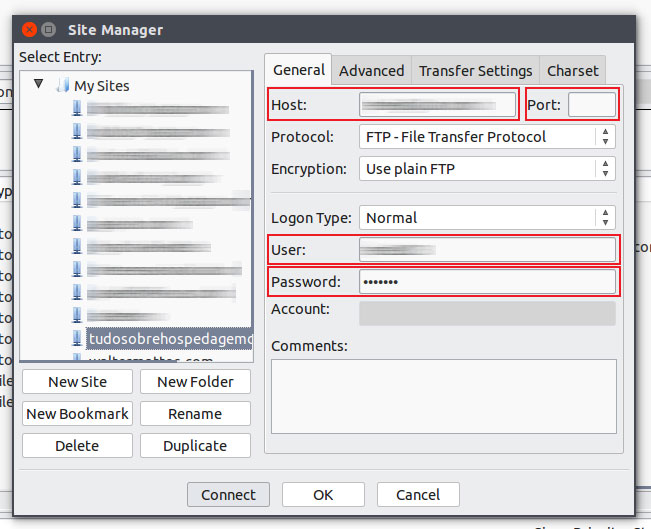
lamp0/web/vhosts/proceed with the steps on how to install and connect to an FTP Server, I will like to briefly describe the difference between active and passive FTP as this is a prevalent question when dealing with Firewall configuration to support the deployment. Public website files should be placed inside the htdocs folder, for example: Navigate to the virtualhost you wish to upload files into, and then you can drag-and-drop files from the local window pane, to the remote window pane, dropping the files into the desired folder. Once here, you will see a bunch of folders that correspond to the name of a website (virtualhost) that you specified to be hosted by your Simple Hosting instance. Now that you’re connected to the instance, you can double-click on the vhosts folder icon to go to where your virtualhosts are located. You will then be connected to your server, and will see a window that displays the contents of your instance (the contents may vary depending on the type of instance and its version). You have no guarantee that the server is the computer you think it isįingerprint: ssh-rsa 2048 35:e0:5a:a9:54:12:55:6b:ce:41:8c:c1:9e:35:1d:f6Ĭlick on “ Always trust this host, add this key to the cache”, and click OK to continue.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
